Capsule Summary
Balanced Crystalloids- A Metanalysis
Emerging evidence suggests that balanced crystalloids which are more balanced with respect to plasma might have some advantages over normal saline particularly with regards to the kidney function. A recently published meta-analysis summarised the evidence comparing different balanced crystalloid solutions.
Objective
Comparing the different balanced crystalloid solutions and comparing the evidence.
Study Methodology:
• This meta-analysis included 24 randomised clinical trials.
• Solutions which were compared included Plasmalyte, Ringer’s Lactate, Ringerfundin, Hartmann’s solution, Ringer’s Bicarbonate, Sterofundin, Kabilyte, Normosol, and novel balanced solutions.
• Out of the 24 studies included, 16 were performed in the peri-operative setting, 6 in the intensive care unit, 1 in the emergency department and 1 in healthy volunteers.
Study Results:
There were 12 studies which compared plasmalyte with other balanced crystalloids (Hartmanns, Ringers Lactate, Sterofundin, Ringerfundin).
The findings were as follows on the different parameters:
• No important differences in post-infusion serum pH or potassium when comparing Plasmalyte with other balanced crystalloids.
• Insufficient data to examine the impact of different balanced crystalloids on patient-important outcomes such as mortality and length of hospitalisation.

Conclusion
• Lower serum concentrations of chloride and lactate, and higher base excess were seen with plasmalyte compared with other balanced crystalloids.
• Certainty of evidence is low.
• Large randomised controlled trials need to be carried out to determine the balanced crystalloid of choice in patients requiring fluid therapy.
Information Source:
You can access the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8133105/
Disclaimer
The information presented in this article is for informational and educational purposesonly and does not substitute professional medical advice and consultation with healthcare professionals.
Copyright Reserved @2021
independent Publication from Biourbexer Solutions. Please contact us at Contact@biourbexer.com for any queries.
Capsule Summary
Effect of Balanced Crystalloids on the Kidney
Crystalloid solutions are widely used in clinical practice for correction of fluid and electrolyte imbalance. Normal saline is the most widely used crystalloid solution. Emerging evidence suggests that balanced crystalloids which are more balanced with respect to plasma might have some advantages over normal saline particularly with regards to the kidney function. A recently published study in BMC Nephrology analysed the effect of balanced crystalloids on urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in critically ill adults.
Objective
To better understand the effect of crystalloid composition on the development of tubular injury.
Study Hypothesis:
• Urinary biomarkers of renal tubular injury would be lower in patients who received balanced crystalloids compared to the patients who received normal saline.
• Study Methodology: An ancillary study was conducted to the Isotonic Solutions and Major Adverse Renal Events Trial (SMART) between February15 to July 15, 2016.
• Compared the effect of balanced crystalloids in comparison with saline on urinary levels of neutrophil gelatinase- associated lipocalin (NGAL) and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) among 261 consecutively-enrolled critically ill adults admitted from the emergency department to the medical ICU.
• Informed consent was received from all the patients.
• Urine samples were collected from the patients 36 ± 12 h after hospital admission.
• NGAL and KIM-1 levels were measured using commercially available ELISAs.
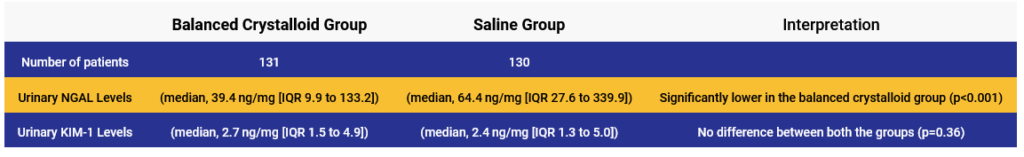
Study Results:
Conclusion
• Patients who received balanced crystalloids had significantly lower urinary concentrations of NGAL and similar urinary concentrations of KIM-1 compared to those who received saline.
• Use of balanced crystalloids resulted in a modest reduction in early biomarkers of acute kidney injury compared with saline.
Information Source:
You can access the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8133105/
Disclaimer
The information presented in this article is for informational and educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice and consultation with healthcare professionals.
Copyright Reserved @2021
You can access the full article at https://bmcnephrol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12882-021-02236-x
Capsule Summary
Balanced Crystalloids in Diabetic Ketoacidosis- A Metanalysis
Normal saline is the most widely used crystalloid solution. There is emerging evidence suggesting that balanced crystalloids which have more physiological levels of sodium and chloride may have certain advantages over normal saline particularly with regards to the development of hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a condition which is characterised by mild to severe metabolic acidosis and a severe fluid deficit. Some studies have suggested that hyperchloremia in patients with DKA may be associated with a longer time to DKA resolution and longer hospital length of stay. (1,2) A recently published meta-analysis summarised the evidence comparing different balanced crystalloid solutions in patients with DKA.
Objective
The primary objective of this systematic review and meta-analysis of Randomised Clinical Trials was to examine the role of saline versus balanced crystalloid in the resuscitation of patients with Diabetic Ketoacidosis.
Study Methodology:
• There were 8 randomised clinical trials which were as part of this meta-analysis.
• Data from 482 patients was analysed.
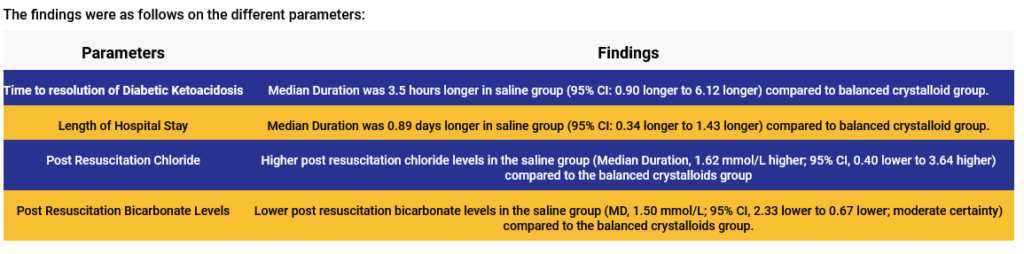
Study Results:
Conclusion
• Use of saline may be associated with longer time to DKA resolution, higher post-resuscitation plasma chloride levels, lower post-resuscitation plasma bicarbonate levels, and longer hospital stay compared with balanced crystalloids.
• Pending further data, low to moderate certainty data supports using balanced crystalloid over saline for fluid resuscitation in patients with DKA.
Information Source:
You can access the full article at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8740878/
References:
1. Goad NT, Bakhru RN, Pirkle JL, et al.: Association of hyperchloremia with unfavorable clinical outcomes in adults with diabetic ketoacidosis. J Intensive Care Med 2019; 35:1307–1313
2. Oliver WD, Willis GC, Hines MC, et al.: Comparison of plasma-lyte A and sodium chloride 0.9% for fluid resuscitation of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. Hosp Pharm 2018; 53:326–330
Disclaimer
The information presented in this article is for informational and educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice and consultation with healthcare professionals.
Copyright Reserved @2021
You can access the full article at https://bmcnephrol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12882-021-02236-x

• The use of balanced salt solutions in the management of the critically ill has focused on the ill effects of Normal Saline in various clinical situations. The recent meta-analysis on its use in patients with ketoacidotic state with Diabetes Mellitus focuses on the advantages of its use in early resuscitation vis-a-vis parameters like time to resolution, hospital Length of Stay, post resuscitation Chloride levels and HCO3 levels. All these are favourable for an acute metabolically deranged state such as ketoacidosis.
• Another recent meta-analysis on the use of balanced salt solutions in the intensive care published in the latest issue of NEJM provides us further evidence. The authors conclude that the estimated effect of using balanced crystalloids versus saline in critically ill adults ranges from a 9% relative reduction to a 1% relative increase in the risk of death, with a high probability that the average effect of using balanced crystalloids is to reduce mortality.1
• Resuscitation with balanced crystalloids demonstrated lower hospital or 28-/30-day mortality compared with saline in critically ill adults but not specifically those with sepsis.The authors conclude that Balanced crystalloids should be provided preferentially to saline in most critically ill adult patients.
• Large volume infusions of crystalloids (nearly 3000 to 7000 milliliters are typically needed) for volume repletion in DKA, especially those with acetate as a buffer help to improve/ stabilize the HCO3 buffer levels . Acetate is rapidly metabolized, generating equimolar amounts of bicarbonate. The major metabolic effects of acetate administration are related to the development of alkalosis. Acetate metabolism in normal human subjects appears to be first order kinetics.2
• In addition to acting to redistribute carbon systemically like a ketone body, it acts as a cellular regulatory molecule with diverse functions beyond the formation of acetyl-CoA for energy derivation and lipogenesis and in part, as a metabolic sensor linking nutrient balance and cellular stress responses with gene transcription and the regulation of protein function.3
• Hence it is reasonable to conclude that acute physiological and metabolic derangements requiring fluid resuscitation are best managed with balanced salt solutions.
References:
1. Hammond DA, Lam SW, Rech MA, Smith MN, Westrick J, Trivedi AP, Balk RA. Balanced Crystalloids versus Saline in Critically Ill Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;54(1):5-13. DOI: 10.1177/1060028019866420. Epub 2019 Jul 31. PMID: 31364382.
2. Richards, R. H., Vreman, H. J., Zager, P., Feldman, C., Blaschke, T., & Weiner, M. W. (1982). Acetate Metabolism in Normal Human Subjects. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 2(1), 47–57. doi:10.1016/s0272-6386(82)80043-7 10.1016/S0272-6386(82)80043-7
3. Moffett JR, Puthillathu N, Vengilote R, Jaworski DM, Namboodiri AM. Acetate Revisited: A Key Biomolecule at the Nexus of Metabolism, Epigenetics and Oncogenesis-Part 1: Acetyl-CoA, Acetogenesis, and Acyl-CoA Short-Chain Synthetases. Front Physiol. 2020 Nov 12;11:580167. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.580167. PMID: 33281616; PMCID: PMC7689297.
Disclaimer
The information presented in this article is for informational and educational purposesonly and does not substitute professional medical advice and consultation with healthcare professionals.
Copyright Reserved @2021
You can access the full article at https://bmcnephrol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12882-021-02236-x
Capsule Summary
Balanced Crystalloids vs Normal Saline in Sepsis: A Metanalysis
• Normal saline is the most widely used crystalloid solution. There is emerging evidence suggesting that balanced crystalloids which have more physiological levels of sodium and chloride may have certain advantages over normal saline, particularly with regard to the development of hypercritical metabolic acidosis
• A recently published meta-analysis compared normal saline and balanced crystalloids in adults with sepsis.
Objective
Conduct a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis to include all relevant studies to assess the effect of Balanced Crystalloids vs Normal Saline on different clinical outcomes for adults with sepsis.
Study Methodology:
• A systematic search of PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Sciences databases through 22 January 2022, was performed for studies that compared Balanced Crystalloids (BC) vs Normal Saline (NS) in adults with sepsis.
• Fifteen studies involving 20,329 patients were included in the analysis.
Study Results:
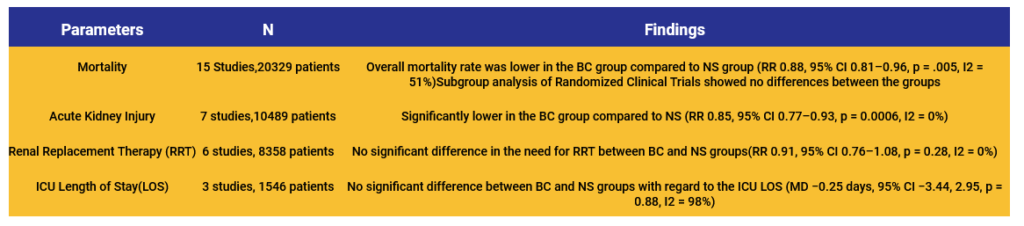
Study outcomes included mortality and acute kidney injury (AKI), need for renal replacement therapy (RRT), and ICU length of stay (LOS).
Conclusion
• Reduced mortality associated with Balanced Crystalloids compared to Normal Saline in patients with Sepsis.
• No significant differences in mortality between the groups when sub-group analysis of RCTs was conducted.
• There was no significant difference in the need for RRT or ICU LOS between BC and NS.
• Pending further data, the current study supports using BC over NS for fluid resuscitation in adults with sepsis.
• Further large-scale RCTs needed to validate the finding
Information Source:
You can access the full article at t https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8133105/